December 2021 (PDF for print)
Patient Demography: Male, 70’s, anemia
Diagnosis: Myelodysplastic Syndrome with Excess Blasts (MDS-EB-1)
Other Information: In peripheral blood - mature neutrophils (Band + Seg.) 60%, myelocytes 14%, blasts 2%, erythroblasts also present, blasts with high N/C ratio, delicate nuclear network structure and nucleoli. In addition, Pseudo-Pelger-Hu?t anomaly, neutrophil with hypogranularity, and giant platelets were also observed, but erythroblasts showed no megaloblastoid changes. In bone marrow aspirate - giant neutrophil with hypogranularity, binucleated erythroblasts, and micromegakaryocytes. We diagnosed MDS-EB-1 based on the percentage of blasts in the peripheral blood.
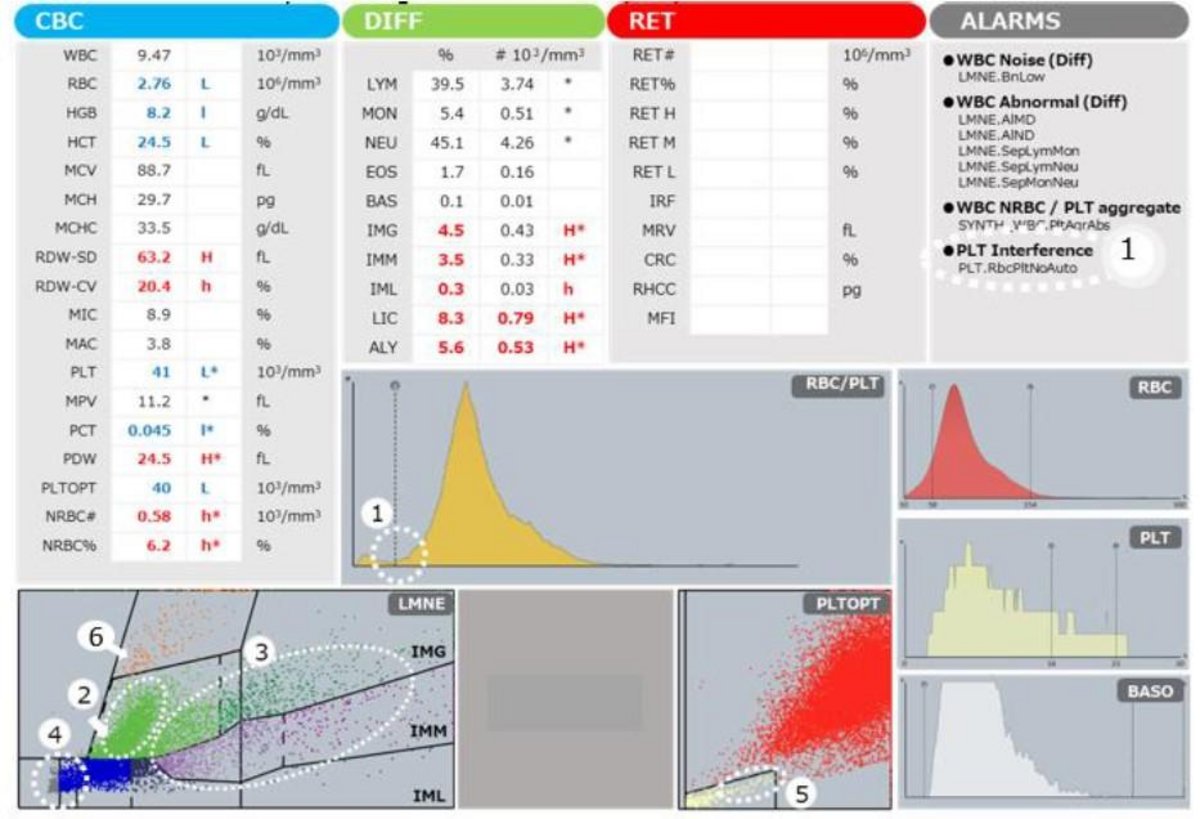
FBC results plus flagging/graphical indicators:
In addition to anemia and thrombocytopenia, the RDW-SD and RDW-CV were high, suggesting abnormalities in the size and morphology of erythrocytes. Raised Large Immature Cells (LIC), especially IMG and IMM, suggesting immature myeloid cells.
? 1. Not clearly separated, suggesting large platelets and schizocytes.
? 2. Neutrophil population.
? 3. Reduced optical absorbance, suggesting neutrophils with hypogranularity and/ or hyposegmentation.
? 4. Populations of large immature cells are seen across the IMG and IMM regions.
? 5. Population indicating the presence of erythroblasts.
? 6. Area suggesting the presence of giant platelets.
This clinical case is provided by Dr. Tohru Inaba, Dept. of Infection Control and Lab. Med., Kyoto Prefectural Univ. of Medicine.
Sie haben Fragen oder Wünsche? Nutzen Sie dieses Formular, um mit unseren Spezialisten in Kontakt zu treten.